10 Essential Steps for Web Application Security Testing
Web app security testing is crucial for protecting sensitive data from cybercriminals who exploit system vulnerabilities.
Updated June 17, 2024

As data breaches increase, web application security testing grows more critical. However, some companies still don't take security seriously. In 2020, Microsoft suffered a massive leak that exposed over 250 million customer support data.
Shockingly, despite soaring breach costs, IBM reports that half of breached organizations won't increase security spending. This can lead to devastating consequences, as breached companies underperform on average.
But with knowledge and cost-effective tools like Jit, web application security testing doesn't have to be daunting. In this article, we'll cover web application security testing types and provide expert insights into 10 fundamental steps to secure your web applications.
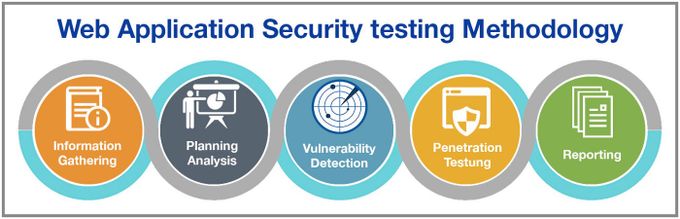
Web Application Security Testing Steps
1. Understand your security testing scope
2. Implement each tool on all resources
3. Implement SSDLC
4. Perform a risk assessment
5. Provide security training for developers
6. Use various security layers
7. Automate security tasks
8. Patch and update regularly
9. Adopt Continuous Security Monitoring tools
10. Document your results
What is Web Application Security Testing?
Web Application Security Testing (WAST) is a series of security tests that ensure your web applications are secure. It involves continuous efforts to identify vulnerabilities across the application's functionalities, focusing mainly on the application layer.
WAST scrutinizes the server configuration, input and output handling, authorization, and authentication credentials.
Why should you consider Web Application Security Testing?
You should consider Web Application Security Testing for the following reasons:
- Businesses need to safeguard their sensitive data against constantly evolving cyber threats.
- It helps businesses understand the potential impact of vulnerabilities and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
- It ensures compliance with regulations such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and SOC 2. These regulations require organizations to protect sensitive data and demonstrate that they have implemented adequate security controls.
» Take a look at the best open-source product security tools
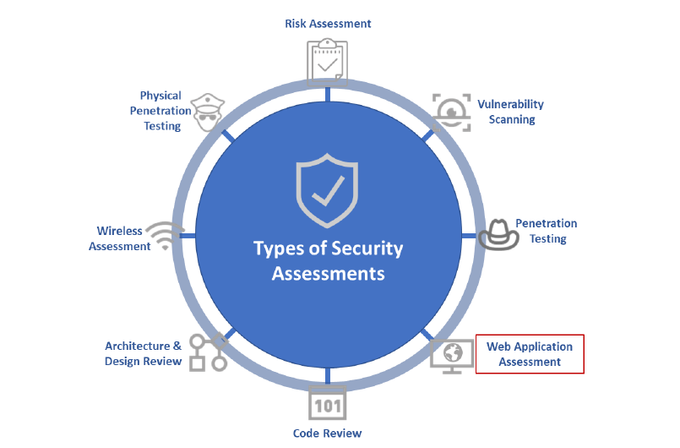
Types of Web Application Security Testing
WAST involves various types that aim to address specific security concerns. These tests can be conducted at different stages of the software development life cycle (SDLC).
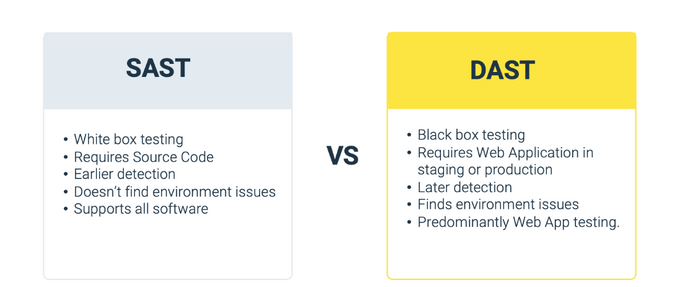
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
Static Application Security Testing (SAST) is a security measure integrated into the development cycle before application deployment. Bandit is one example of this measure. SAST can be automated and run during the build process to ensure security measures are in place.
Best SAST tools analyze the application's code and identify potential vulnerabilities without the application needing to run. They look for vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
Jit makes it easy for developers to integrate continuous SAST into their cycles by integrating security scanning and remediation within their IDE or Source Code Manager:
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) is a tool that simulates real-world attacks on an application and identifies potential vulnerabilities. They are used during the testing phase of SDLC to detect security flaws.
Common DAST tools include OWASP ZAP and Legitify by Legit Labs. These tools can identify vulnerabilities in application configuration that are absent in the source code. They can also detect runtime issues like misconfigured servers.
ZAP is an outstanding tool for surfacing vulnerabilities in runtime, but it can be difficult to configure. If you're looking for a quick and easy to way to deploy DAST, learn more about Jit's configuration wizard that deploys ZAP in a matter of minutes
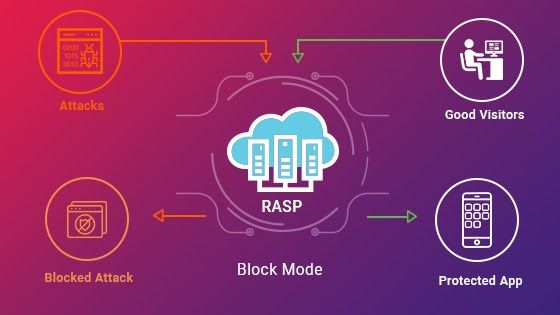
Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP)
Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) constantly monitors the runtime environment of a web application to identify and prevent security threats.
RASP has the ability to identify vulnerabilities that are not present in the source code. These vulnerabilities may only appear when the application is configured and running. RASP is the last line of defense that helps ensure the security of your web application.
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing is like a thrilling game of cat and mouse between ethical hackers and your web application's defenses. Expert ethical hackers, known for their mastery in uncovering vulnerabilities in a target system, typically conduct penetration testing on the application to ensure its security.
By simulating a real-world attack, penetration testing can help identify vulnerabilities that other methods may miss. It can also help organizations understand how an attacker might exploit a vulnerability and take steps to mitigate the risk.
10 Essential Steps for Web Application Security Testing
To properly perform web application security testing, these are ten essential steps that you should follow:
1. Understand your security testing scope
Understanding your security testing scope includes identifying the web applications for testing, the types of testing required, and the necessary resources.
Testing requires a clear and defined scope to ensure that all critical areas are covered and resources are not wasted on unnecessary testing. A well-defined scope will also help you set realistic metrics for the testing process and prioritize vulnerabilities the security testing scope must address.
2. Implement each tool on all resources
Selection and maintenance of specific tools are critical to web security. However, configuration, monitoring, and seamless pipeline integration are also important.
Each tool requires unique implementation, configuration, and management, which can be complex. Jit simplifies this by allowing easy security tool integration at each CI/CD pipeline stage, all monitored from a single platform.
3. Implement SSDLC
SSDLC emphasizes prioritizing security throughout the entire software development process, from gathering initial requirements to deployment. It involves incorporating security requirements into the development process, conducting regular security testing, and implementing security controls to ensure secure software.
4. Perform a risk assessment
Performing a risk assessment includes gathering information about potential vulnerabilities and threats, how often they may appear, and their impacts. The tester can then use this information to prioritize vulnerabilities that need to be addressed and develop a plan to mitigate those vulnerabilities.
5. Provide security training for developers
Developers are crucial in securing web applications, but 30% feel their security training can improve. They need proper training to write secure code and identify potential vulnerabilities.
Jit is a platform that offers a native dev experience, running on PRs to highlight in-context vulnerabilities. It additionally provides remediation suggestions in real-time, further making web applications more secure for everyone.
6. Use various security layers
It is important to incorporate multiple layers of security throughout all phases of SDLC, not just during the testing stage. Utilizing a variety of security measures, such as those mentioned earlier, helps to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. The more security layers used, the better the overall protection.
7. Automate security tasks
Automating security tasks like vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and compliance checks ensures regularity and promptness. It also reduces the workload for security and engineering teams, freeing them to focus on critical tasks. Jit simplifies this automation process and integrates security tools into the software development process. It acts as a command center that controls all security functions.
8. Patch and update regularly
Regularly patching and updating web applications is a crucial step in minimizing security risks. By doing so, known vulnerabilities are addressed, and the web application is equipped with the latest security features. It may seem like a basic measure (and it is!), but it is often overlooked. It's essential to plan for each update to avoid any compatibility issues between APIs.
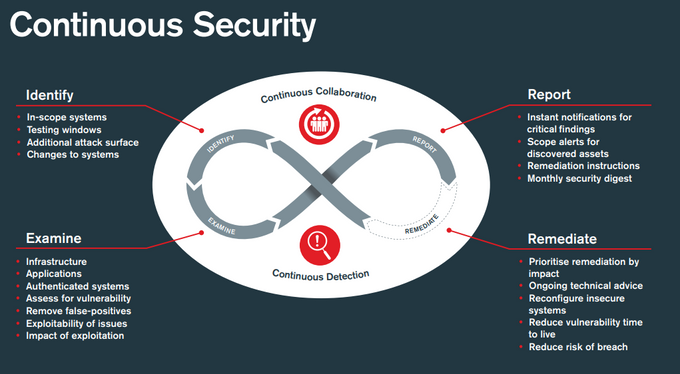
9. Adopt Continuous Security Monitoring tools
Traditional security controls like firewalls and antivirus software are no longer enough to detect real-time threats. Continuous security monitoring tools are crucial for round-the-clock visibility and real-time detection of potential threats and vulnerabilities. These tools help take the pressure off developers by automating most of the processes and enable organizations to mitigate risks proactively.
10. Document your results
Conducting security testing and documenting the vulnerabilities identified, actions taken to address them, and any consequences of the testing. This helps track progress, identify recurring issues, and comply with industry regulations. This demonstrates the company's commitment to security.
DORA Metrics, such as Change Failure Rate (CFR), Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR), and Detection Rate. Regularly tracking these metrics can help you keep up with fast-paced engineering processes.
To better understand DevSecOps processes, measuring and benchmarking security and documenting these efforts is crucial. By measuring security in quantifiable terms, you can identify areas for improvement and determine what needs to be changed.
Don't leave Web Application Security to chance
Web application security is critical and cannot be left to chance. While security experts may have different approaches to protecting web applications, some measures are essential.
Implementing basic security measures and equipping your team with the right tools can initially seem overwhelming, but it will make the process easier. Producing secure software is a win for everyone. Get started for free with Jit and learn how it can help you master your application security toolchain.